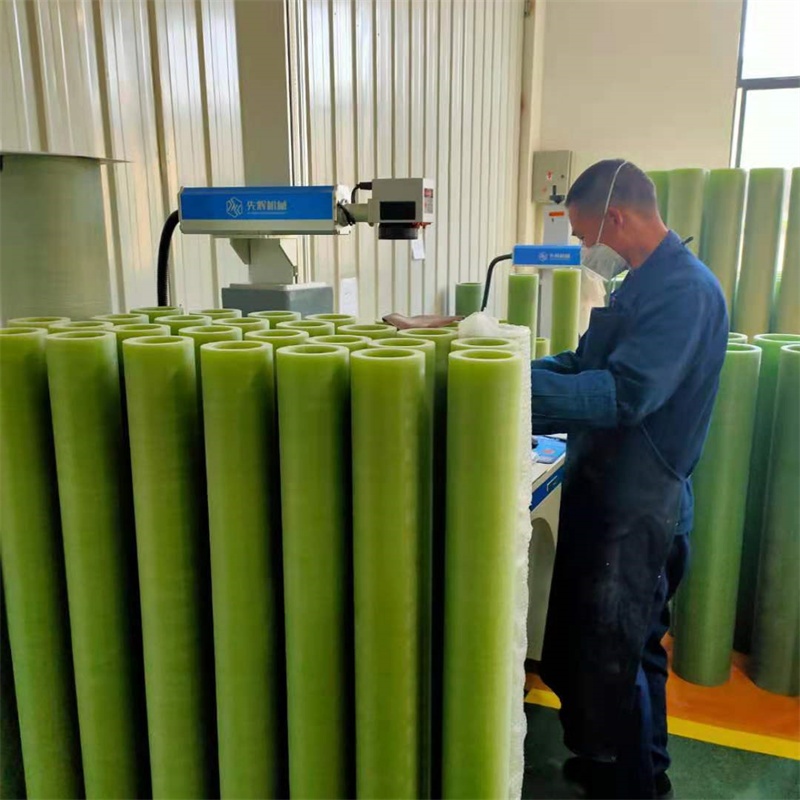
The process of manufacturing FRP tubes
Introduction
(Fiber reinforced plastic), or FRP, tubes are composite materials made up of a polymer matrix and reinforcing fibers such as glass, carbon, or basalt. They are commonly used in a variety of industrial applications for their exceptional strength, durability, and ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions. In this article, We will explore the manufacturing process of FRP tubes, the materials and equipment required, quality control measures involved, and applications of FRP tubes in different industries.
Materials and Equipment
Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process for FRP tubes is a multi-step process that involves the following stages:
1. Preparation of raw materials: The first step involves preparing the raw materials for fabrication. The resin is mixed with any additives using a resin mixer, and the reinforcing fibers are cut to the appropriate length and loaded onto the winding machine.
2. Resin mixing and application: The resin and any additives are mixed together to form a homogeneous mixture, which is then applied to the reinforcing fibers as they are wound around a mandrel or core.
4. Curing process: Once the fabric is wrapped around the mandrel or core, it is loaded into a curing oven where heat is applied to cure the composite material. The curing process is usually controlled to ensure that the composite material sets at the correct temperature and for the correct amount of time.
5. Cutting and finishing: After the composite material has been cured, it is removed from the mandrel or core and cut to the desired length. The tube is then finished by grinding, sanding or polishing to achieve the desired surface finish.

Quality Control Measures
1. Inspection and testing of raw materials: The raw materials are inspected and tested to ensure that they meet the required quality standards, such as the strength and stiffness of the fibers and the chemical composition of the resin.
2. Quality checks during fabrication: Quality checks are conducted during the manufacturing process to ensure that the composite materials are manufactured according to the required specifications. This includes checking the curing temperature and time, the winding pattern, and the thickness of the composite material.
3. Testing and validation of finished FRP tubes: The finished FRP tubes are tested and validated to ensure that they meet the required standards for strength, stiffness, and other performance criteria. This includes testing for compression, bending, torsion, and shear strength, as well as other properties such as thermal and fatigue resistance.
Applications of FRP Tubes
2. Infrastructure and construction: FRP tubes are used in bridges, buildings, and other infrastructure projects because of their high strength-to-weight ratio, durability, and resistance to weathering.
3. Renewable energy sector: FRP tubes are used in wind turbine blades, hydroelectric power plants, and other renewable energy applications because of their exceptional strength, durability, and ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions.
Advantages of FRP Tubes
1. Lightweight and durable: FRP tubes are lighter than steel and concrete, making them more convenient to transport, install and maintain. Additionally, FRP tubes are durable, and they can last for several years before needing to be replaced.
2. Corrosion resistant: FRP tubes are highly resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for use in harsh environments that are characterized by harsh chemicals, saltwater, and humidity.
3. Low maintenance: FRP tubes require less maintenance than traditional materials such as steel, concrete or aluminum. Repairs can be done easily without the need for specialized equipment or tools.



